CCC Study material in English
Hello friends in this article you can find your query related to CCC Study material in English, Computer Basic Knowledge, CCC Notes pdf in English 2025, Computer kya hai, Computer Full form, Computer fundamentals, CCC Study material
Computer Basic Knowledge
 |
| CCC Study Material in English |
CCC Notes pdf in English 2025
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER
INTRODUCTION
Let
us begin with the word ‘Compute’. It
means ‘to calculate’. We all are familiar with calculations in our day to day
life. We apply mathematical operations like addition, subtraction,
multiplication, etc. and many other formulae for calculations. Simpler
calculations take less time. But complex calculations take much longer time.
Another
factor is accuracy in calculations. So man explored with the idea to develop a
machine which can perform this type of arithmetic calculation faster and with
full accuracy. This gave birth to a device or machine called ‘Computer’.
WHAT IS A COMPUTER?
Computer
is an electronic device. As mentioned in the introduction it can do arithmetic
calculations faster. But as you will see later it does much more than that.
Therefore, we may define computer as a device that transforms
data. Data can be anything like marks obtained by you in various subjects.
It can also be name, age, sex, weight, height, etc.
 |
| Computer System |
Fig. 1.1
Computer Full Form:
C - Common
O - Operational
M - Machine
P - Particularly
U - Used
for
T - Training
E - Education
R - Research
So we can define Computer as a Common Operational Machine Particularly Used for Training, Education and Research.
HISTORY OF COMPUTER
Calculating Machines
It took over generations for early man to build mechanical devices
for counting large numbers. The first calculating device called ABACUS was
developed by the Egyptian and Chinese people.
 |
| Abacus Calculating Machine |
Fig. 1.2
Babbage’s Analytical Engine
It was in the year 1823 that a
famous English man Charles Babbage built a mechanical machine to do complex
mathematical calculations. It was called difference engine. Later he
developed a general-purpose calculating machine called analytical engine.
You should know that Charles Babbage is called the father of computer.
Modern Electronic Calculator
The electronic calculator used in 1960 s was run with electron
tubes, which was quite bulky. Later it was replaced with transistors and
as a result the size of calculators became too small.
COMPUTER GENERATIONS
1. First Generation Computers (1940-1956)
First generation computers used Vacuum Tubes. These computers were large in size and writing
programs on them was difficult.
Example-
ENIAC: Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator
UNIVAC: Universal
Automatic Calculator
 |
| Vacuum Tube |
Fig.
1.3
2. Second Generation Computers (1956-1963)
Around 1955 a device called Transistor replaced the vacuum tubes in the first generation computer. Transistors are smaller than vacuum tubes and have higher operating speed.
It is in the second generation that the concept of Central
Processing Unit (CPU), memory, programming language and input and output units
were developed. The programming languages such as COBOL, FORTRAN were developed
during this period.
 |
| Transistor |
Fig.
1.4
Example:
IBM 1620, IBM 1401
3. Third Generation Computers (1964-1971)
The third generation computers were introduced in 1964. They used Integrated Circuits (ICs). These ICs are popularly known as Chips. A single IC has many transistors, registers and capacitors built on a single thin slice of silicon.
Computers
of this Generation were small in size, low cost, large memory and processing
speed is very high.
Example: IBM-360,
ICL-1900, IBM-370, and VAX-750.
Higher level language such as BASIC (Beginners All Purpose
Symbolic Instruction Code) was developed during this period.
 |
| Integrated Circuits |
Fig.
1.5
4. Fourth Generation Computers (1971-1985)
The present day computers that you see today are the fourth generation computers that started around 1975. It uses Large Scale Integrated Circuits (LSIC) built on a single silicon chip called microprocessors.
Due to the development
of microprocessor it is possible to place computer’s central processing unit
(CPU) on single chip. These computers are called microcomputers. Later Very
Large Scale Integrated Circuits (VLSIC) replaced LSICs.
The
personal computer (PC) that you see in your school is a Fourth Generation
Computer.
5. Fifth Generation Computer (1986-Present)
The computers of 1990s are said to be Fifth Generation computers.
The speed is extremely high in fifth generation computer. Apart from this it
can perform parallel processing. The concept of Artificial intelligence has been introduced to allow
the computer to take its own decision. It is still in a developmental stage.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTER
1. Speed
As you know computer can work very fast. It takes only few seconds for calculations that we take hours to complete. Suppose you are asked to calculate the average monthly income of one thousand persons in your neighborhood.
For
this you have to add income from all sources for all persons on a day to day
basis and find out the average for each one of them. How long will it take for
you to do this? one day, two days or one week? Do you know your small computer
can finish this work in few seconds?
2. Accuracy
Suppose someone calculates faster but commits a lot of errors in computing. Such result is useless. There is another aspect. Suppose you want to divide 15 by 7. You may work out up to 2 decimal places and say the dividend is 2.14. I may calculate up to 4 decimal places and say that the result is 2.1428. Someone else may go up to 9 decimal places and say the result is 2.142857143.
Hence, in
addition to speed, the computer should have accuracy or correctness in
computing. The degree of accuracy of computer is very high and every
calculation is performed with the same accuracy.
3. Power of Remembering
Computer
has the power of storing any amount of information or data. Any information can
be stored and recalled as long as you require it, for any numbers of years.
4. No IQ
Computer is a dumb machine and it cannot do any work without
instruction from the user. It performs the instructions at tremendous speed and
with accuracy. It is you to decide what you want to do and in what sequence. So
a computer cannot take its own decision as you can.
5. No Feeling
It does not have feelings or emotion, taste, knowledge and
experience. Thus it does not get tired even after long hours of work. It does
not distinguish between users.
6. Storage
The Computer has an in-built memory where it can store a large
amount of data. You can also store data in secondary storage devices such as
floppies, which can be kept outside your computer and can be carried to other
computers.
TYPES OF COMPUTERS
A) Analog Computers: An Analog computers handle or process information which is of a physical nature, for example – Temperature, pressure etc.
B) Digital Computers: Digital Computers process information which is essentially in a binary or two state form, namely ‘0’ (zero) and ‘1’ (one).
Although they belong to the fifth generation they can be divided into different categories depending upon the size, efficiency, memory and number of users.
1. Microcomputer: Microcomputer is at the lowest end of the computer range in terms of speed and storage capacity. The size of these computers is very small.
2. Mini Computer: This is designed to support more than one user at a time. It possesses large storage capacity and operates at a higher speed.
3. Mainframes: These types of computers are generally 32-bit microprocessors. They operate at very high speed, have very large storage capacity and can handle the work load of many users.
4. Supercomputer: They are the fastest and most expensive machines. They have high processing speed compared to other computers. They have also multiprocessing technique.
Supercomputers are mainly being used for whether forecasting, biomedical research, remote sensing, aircraft design and other areas of science and technology. Examples of supercomputers are CRAY YMP, CRAY2, NEC SX-3, CRAY XMP and PARAM from India.
C) Hybrid Computers: Hybrid computers are made by combining features of analog computers and digital computers.
APPLICATIONS OF COMPUTER
Today computers are use everywhere like Banking, Railway’s,
School, Universities, Hospitals, offices etc.
COMPONENTS OF
COMPUTER SYSTEM:
1. Input: This is the
process of entering data and programs into the computer system. An input is the
process by which we give some instructions to the system to perform a
particular task.
2. Processing: The task of
performing operations like arithmetic and logical operations is called
processing. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) takes data and instructions from
the storage unit and makes all sorts of calculations based on the instructions
given and the type of data provided. It is then sent back to the storage unit.
3. Output: This is the
process of producing results from the data for getting useful information.
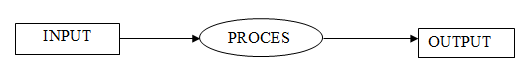 |
| Input Output Process |
Fig.
1.6
FUNCTIONAL
UNITS:
The computer system is divided into three separate units for its
operation.
1) Arithmetic logical unit,
2) Control unit, and
3) Central processing unit.
1. Arithmetic Logical Unit (ALU)
After you enter data through the input device it is stored in the
primary storage unit. The actual processing of the data and instruction are
performed by Arithmetic Logical Unit. The major operations performed by the ALU
are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, logic and comparison.
2. Control Unit (CU)
The next component of computer is the Control Unit, which acts
like the supervisor seeing that things are done in proper fashion. The control
unit determines the sequence in which computer programs and instructions are
executed.
3. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The ALU and the CU of a computer system are jointly known as the
central processing unit. You may call CPU as the brain of any computer system.
It is just like brain that takes all major decisions.
 |
| Processor |
Fig. 1.7 CPU
(Processor)
Personal Computer Configuration
Now
let us identify the physical components that make the computer work. These are
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
2. Computer Memory (RAM and ROM)
3. Data bus
4. Ports
5. Motherboard
6. Hard disk
7. Output Devices
8. Input Devices
All these components are inter-connected for the personal computer to work.
Also Read:
👉 CCC Question Answer in Hindi English pdf download
👉 Digital Financial Tools and Applications Questions and Answers
Related Searches: Computer in Hindi, Computer kya hai, Computer basic knowledge, Computer Full form, Computer fundamentals, CCC Computer course, CCC Study material, CCC Notes pdf in English 2025, Computer courses basic











Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box